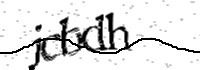
Please type the text you see in the image into the text box and submit. Refresh the page to generate a new image.
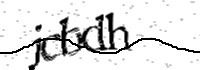
Note: Access to this domain may require javascript and cookies to be enabled. If you arrived here while submitting a form, you may have to re-submit the form.
Or call us at 800-809-4217